A rheumatologist specializes in muscle pain. They diagnose and treat musculoskeletal and autoimmune conditions.
Muscle pain can affect daily life significantly. Rheumatologists focus on disorders causing muscle and joint pain. They treat conditions like arthritis, lupus, and fibromyalgia. Seeking a specialist ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Chronic muscle pain often requires expert care.
Rheumatologists use advanced techniques for pain management. Early intervention can prevent complications. Comprehensive care includes medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Consult a rheumatologist for persistent muscle pain. They provide tailored treatment plans to improve quality of life.
Types Of Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can affect anyone. Understanding the type of muscle pain can help identify the right specialist for treatment. There are two main types of muscle pain: acute and chronic. Knowing the difference between these can lead to better diagnosis and care.
Acute Muscle Pain
Acute muscle pain is sudden. It usually results from an injury or overuse. This type of pain often happens during activities like sports, heavy lifting, or sudden movements.
Common causes of acute muscle pain include:
- Strains and sprains
- Muscle tears
- Overexertion
- Injuries from accidents
Symptoms of acute muscle pain are:
- Sudden sharp pain
- Swelling or bruising
- Limited movement
- Tenderness in the affected area
Treatment for acute muscle pain often includes:
- Resting the affected muscle
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers
- Physical therapy for severe cases
Doctors who specialize in acute muscle pain are:
| Specialist | Description |
|---|---|
| Orthopedic Surgeon | Treats musculoskeletal injuries |
| Sports Medicine Physician | Focuses on sports injuries and physical fitness |
Chronic Muscle Pain
Chronic muscle pain lasts for a long time. It can be constant or come and go. This type of pain often results from conditions that affect the muscles over a long period.
Common causes of chronic muscle pain include:
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Myofascial pain syndrome
- Long-term repetitive strain
Symptoms of chronic muscle pain are:
- Aching and stiffness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty sleeping
- Depression due to long-term pain
Treatment for chronic muscle pain often includes:
- Medications for pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Regular exercise and stretching
Doctors who specialize in chronic muscle pain are:
| Specialist | Description |
|---|---|
| Rheumatologist | Specializes in autoimmune and musculoskeletal diseases |
| Pain Management Specialist | Focuses on long-term pain management |
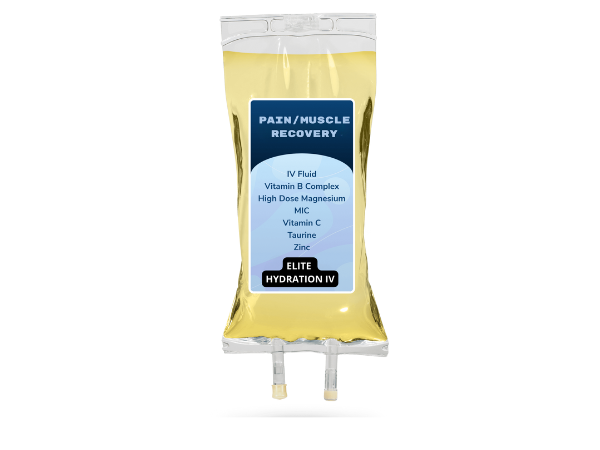

IV Therapy for Muscle Recovery
The benefits of IV Therapy for Muscle Recovery are vast and impactful, making it a preferred choice for many.
Common Causes Of Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can be a frustrating and debilitating condition. Various doctors specialize in diagnosing and treating muscle pain, such as rheumatologists, orthopedists, and physiatrists. Understanding the common causes of muscle pain can help you identify the right specialist for your needs. Here are some common causes of muscle pain that you should be aware of.
Overuse Or Injury
Overuse or injury is one of the most common causes of muscle pain. Engaging in physical activities without proper warm-up can lead to muscle strain and fatigue. Overuse injuries typically occur due to repetitive motion or excessive strain on a particular muscle group.
- Strains and Sprains: These occur when muscles or ligaments are stretched beyond their capacity.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons due to repetitive motion.
- Stress Fractures: Small cracks in bones caused by repetitive force or overuse.
It’s crucial to allow your muscles time to rest and recover. Overworking them can lead to chronic pain and long-term damage. Here is a simple table summarizing common overuse injuries:
| Injury Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Strain | Overstretching or tearing of muscle fibers |
| Sprain | Overstretching or tearing of ligaments |
| Tendinitis | Inflammation of tendons |
| Stress Fracture | Small bone cracks due to repetitive force |
Muscle Tension
Muscle tension often results from stress, poor posture, or repetitive activities. This condition can cause muscles to become tight and sore, often leading to chronic pain. Stress and anxiety are significant contributors to muscle tension.
Here are some common causes of muscle tension:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can lead to physical muscle tension.
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing incorrectly can strain muscles.
- Repetitive Activities: Tasks that involve repetitive motion can cause muscle stiffness.
Managing stress and maintaining good posture are essential in preventing muscle tension. Regular exercise, stretching, and relaxation techniques can help alleviate muscle stiffness and pain.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread muscle pain, fatigue, and tenderness. This condition affects the muscles and soft tissues and often comes with other symptoms such as sleep disturbances and cognitive difficulties.
Key symptoms of fibromyalgia include:
- Widespread Pain: Pain is felt throughout the body, often described as a constant dull ache.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Cognitive Issues: Difficulty concentrating, often referred to as “fibro fog.”
Managing fibromyalgia typically involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. It’s crucial to consult a rheumatologist for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Infections
Infections can also lead to muscle pain. Viral and bacterial infections can cause inflammation and soreness in the muscles. Common infections that cause muscle pain include influenza, Lyme disease, and myositis.
Here are some infections that can cause muscle pain:
- Influenza: Muscle aches and pains are common symptoms of the flu.
- Lyme Disease: This bacterial infection can lead to joint and muscle pain.
- Myositis: Inflammation of the muscles, often caused by infections or autoimmune conditions.
It’s vital to seek medical attention if you experience severe muscle pain accompanied by other symptoms like fever, swelling, or redness. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing infection-related muscle pain.
When To See A Doctor
Dealing with muscle pain can be frustrating and debilitating. Knowing what doctor specializes in muscle pain can help you get the right treatment. Muscle pain can stem from various causes, and self-care measures might not always be enough. Understanding when to see a doctor ensures you get the timely help you need.
Symptoms That Require Medical Attention
Some muscle pain symptoms should not be ignored. These signs might indicate a more serious condition. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Here are the symptoms that need a doctor’s attention:
- Severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest or over-the-counter medications
- Swelling or redness around the painful area
- Experiencing numbness or tingling in the affected muscles
- Muscle pain that follows a traumatic injury, like a fall or accident
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few days
- Signs of an infection, such as fever, chills, or an open wound
- Difficulty moving the affected area or loss of function
These symptoms might indicate conditions like muscle tears, infections, or nerve issues. Ignoring these signs can lead to complications. Consulting a doctor specializing in muscle pain, such as a rheumatologist, orthopedic specialist, or neurologist, is crucial.
When Self-care Measures Don’t Work
Sometimes, self-care measures like rest, ice packs, and over-the-counter pain relievers are not enough. If these methods fail to relieve your muscle pain, it’s time to consult a doctor. Here are scenarios where self-care might fall short:
- Home remedies and self-care have not improved your pain after a week
- Over-the-counter medications provide temporary relief but the pain returns
- The pain interferes with daily activities and quality of life
- Muscle pain that worsens over time, even with self-care
- Recurring muscle pain despite following recommended self-care measures
In such cases, a doctor can diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments. They might suggest physical therapy, prescription medications, or other interventions. A specialist can also help develop a long-term pain management plan. Don’t let persistent muscle pain hinder your life. Seeking medical advice ensures you get the right care and relief.
Types Of Doctors Who Treat Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can be a common issue for many people. It can be caused by various factors, including overuse, injury, or underlying medical conditions. Knowing which doctor to see for muscle pain can be confusing. Here, we’ll explore the different types of doctors who treat muscle pain and how they can help you.
Primary Care Physician
Your Primary Care Physician (PCP) is often the first point of contact for muscle pain. They can diagnose and treat many common muscle issues. If necessary, they can refer you to specialists.
Primary Care Physicians can help with:
- Initial Diagnosis: They perform physical exams and ask about your symptoms.
- Basic Treatments: They may suggest rest, ice, or over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Referrals: They refer you to specialists if the pain persists or is severe.
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Identify the cause of muscle pain |
| Treatment | Provide basic pain relief and advice |
| Referral | Refer to specialists if needed |
Physical Therapist
Physical Therapists specialize in helping patients improve their movement and manage pain through physical methods. They create personalized exercise plans to address muscle pain.
Physical Therapists focus on:
- Rehabilitation: Helping you recover from injuries.
- Exercise Plans: Creating routines to strengthen muscles.
- Pain Management: Using techniques like massage and heat therapy.
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Rehabilitation | Assist in recovery from muscle injuries |
| Exercise | Create and guide through personalized exercise plans |
| Pain Management | Use physical methods to manage pain |
Orthopedist
Orthopedists are doctors who focus on the musculoskeletal system, which includes muscles, bones, and joints. They can treat severe muscle pain and injuries.
Orthopedists specialize in:
- Surgical Treatments: Performing surgeries if needed.
- Medical Interventions: Prescribing medications for pain relief.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Using imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs.
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Perform operations for severe muscle issues |
| Medication | Prescribe drugs for pain management |
| Diagnostics | Use advanced imaging to diagnose conditions |
Rheumatologist
Rheumatologists treat autoimmune and inflammatory conditions that can cause muscle pain, such as arthritis and lupus. They manage chronic pain and systemic issues.
Rheumatologists focus on:
- Chronic Conditions: Treating long-term muscle pain.
- Inflammation Control: Using medications to reduce inflammation.
- Comprehensive Care: Managing multiple symptoms across the body.
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Chronic Pain | Manage long-term muscle pain conditions |
| Inflammation | Control inflammation with medications |
| Comprehensive Care | Provide holistic care for systemic issues |
Choosing A Doctor For Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can be distressing and affect daily life. Choosing the right doctor to address muscle pain is crucial for effective treatment. This guide will help you understand what to look for in a doctor specializing in muscle pain.
Experience And Training
When choosing a doctor for muscle pain, consider their experience and training. Doctors who specialize in muscle pain often have extensive training in fields like rheumatology, orthopedics, or physical medicine. They are well-versed in diagnosing and treating various muscle-related issues.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Look for doctors who have completed a residency in a relevant field.
- Consider if they have pursued fellowships focusing on muscle pain.
- Check their certifications and affiliations with professional organizations.
A table summarizing these points might help:
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Residency | Completed in Rheumatology, Orthopedics, or Physical Medicine |
| Fellowships | Specialized training in muscle pain |
| Certifications | Board-certified in relevant specialties |
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are essential when selecting a doctor for muscle pain. A good doctor listens to your concerns and explains treatment options clearly. They should be approachable and willing to answer questions.
Consider these aspects:
- Does the doctor listen to your symptoms and concerns attentively?
- Do they explain medical terms and procedures in an understandable way?
- Are they open to discussing various treatment options?
Good communication fosters a trusting relationship between you and your doctor. It ensures you understand your condition and treatment plan, leading to better outcomes.
Treatment Philosophy
A doctor’s treatment philosophy plays a crucial role in managing muscle pain. Some doctors prefer a conservative approach, focusing on lifestyle changes and physical therapy. Others might advocate for more aggressive treatments, including medications or surgery.
Consider these points:
- Does the doctor emphasize holistic and non-invasive treatments?
- Are they open to alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care?
- Do they provide a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs?
Understanding a doctor’s treatment philosophy helps you align your preferences with their approach, ensuring a collaborative and effective treatment journey.
Diagnosing Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can affect your daily life and finding the right doctor is crucial. Diagnosing muscle pain involves several steps to identify the root cause and develop an effective treatment plan. Let’s delve into the essential aspects of diagnosing muscle pain.
Medical History
Doctors begin by taking a detailed medical history. This step helps understand the patient’s background and the circumstances leading to the pain. Important questions include:
- When did the pain start?
- What activities trigger the pain?
- Is the pain constant or intermittent?
- What is the intensity and nature of the pain?
- Are there any other symptoms?
Family history also plays a role. If close relatives have conditions like arthritis or fibromyalgia, it can influence the diagnosis. Medications and past treatments are also considered. Previous injuries or surgeries can provide clues about ongoing pain issues.
The information gathered from the medical history helps doctors form an initial diagnosis. They can then decide on the next steps for a thorough examination.
Physical Examination
The next step is a physical examination. Doctors check for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and muscle strength. This examination often includes:
- Inspecting the painful area for swelling or redness.
- Palpating the muscles to identify tender spots.
- Assessing the range of motion in affected joints.
- Testing muscle strength and reflexes.
- Observing the patient’s posture and gait.
Doctors may ask patients to perform specific movements to pinpoint the source of pain. They look for asymmetry and abnormalities in muscle function. This hands-on approach provides valuable insights into the condition.
Diagnostic Tests
When more information is needed, doctors turn to diagnostic tests. These tests help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. Common diagnostic tests include:
- X-rays: Reveal bone issues and joint abnormalities.
- MRI scans: Provide detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles and ligaments.
- Blood tests: Detect inflammation markers and other abnormalities.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures muscle electrical activity to identify nerve or muscle disorders.
- Ultrasound: Visualizes muscle and tendon structures in real-time.
These tests offer a comprehensive view of the musculoskeletal system. They help doctors make accurate diagnoses and develop tailored treatment plans. Combining medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests ensures a thorough evaluation of muscle pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Type Of Doctor To See For Muscle Pain?
See a primary care doctor for initial evaluation. They may refer you to a rheumatologist, orthopedist, or physical therapist.
Which Dr Is Best For Muscle Pain?
A pain specialist or orthopedic doctor is best for muscle pain. They diagnose and treat muscle injuries effectively.
What Is The Best Doctor For Muscle And Joint Pain?
A rheumatologist specializes in muscle and joint pain. They diagnose and treat arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and musculoskeletal disorders.
What Is A Doctor Who Specializes In Muscles Called?
A doctor who specializes in muscles is called a physiatrist or a physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) physician.
Conclusion
Finding the right doctor for muscle pain can greatly improve your quality of life. Specialists like rheumatologists, orthopedists, and physiatrists offer targeted treatments. Always consult a healthcare professional to address your specific needs. Effective treatment starts with the right expertise.
Prioritize your health by choosing the appropriate specialist for your muscle pain.